Device Placement Optimization with Reinforcement Learning
International Conference on Machine Learning, 2017
DOI: NA
Abstract
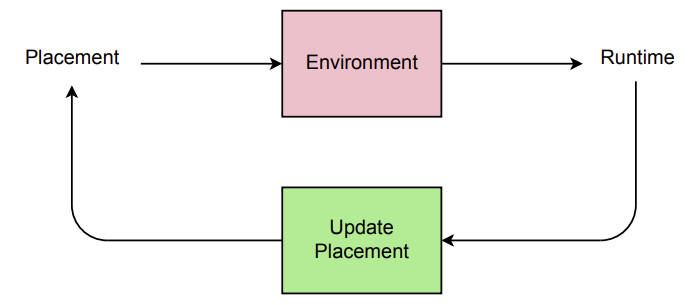
The past few years have witnessed a growth in size and computational requirements for training and inference with neural networks. Currently, a common approach to address these requirements is to use a heterogeneous distributed environment with a mixture of hardware devices such as CPUs and GPUs. Importantly, the decision of placing parts of the neural models on devices is often made by human experts based on simple heuristics and intuitions. In this paper, we propose a method which learns to optimize device placement for TensorFlow computational graphs. Key to our method is the use of a sequence-to-sequence model to predict which subsets of operations in a TensorFlow graph should run on which of the available devices. The execution time of the predicted placements is then used as the reward signal to optimize the parameters of the sequence-to-sequence model. Our main result is that on Inception-V3 for ImageNet classification, and on RNN LSTM, for language modeling and neural machine translation, our model finds non-trivial device placements that outperform hand-crafted heuristics and traditional algorithmic methods.